R-Loops Play Dual Role in Genome Stability and Disease
SHANNON, CLARE, IRELAND, April 20, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ --
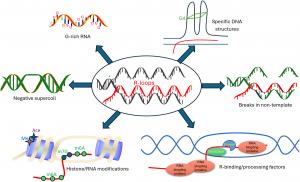
This new review article highlights the pivotal and paradoxical role of R-loops in maintaining genomic stability while simultaneously posing risks to it. These three-stranded nucleic acid structures, composed of an RNA:DNA hybrid and a displaced DNA strand, are now recognized not merely as byproducts of transcription but as essential regulatory elements in gene expression, DNA replication, and repair mechanisms.
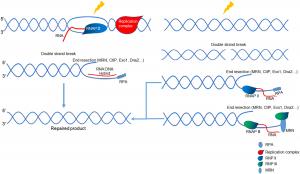
The article traces the evolution of R-loop research, illuminating how sophisticated detection techniques have transformed our understanding of their biological functions. From early antibody-based imaging to high-throughput sequencing methods like DRIP-seq and R-ChIP, the field has advanced rapidly. These tools have revealed the extensive presence of R-loops at key genomic regions such as promoters, terminators, and double-strand break (DSB) sites, positioning them as significant actors in the DNA damage response.
A central focus of the article is the dual nature of R-loops. Under controlled conditions, they play protective roles—regulating gene activity, terminating transcription, and facilitating repair through homologous recombination. However, when dysregulated, R-loops become hazardous. They can obstruct replication forks, induce transcription-replication collisions, and provoke DSBs, ultimately threatening genome integrity. These pathological consequences are amplified in the context of mutations in repair-related genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2, underlining their relevance in diseases such as cancer and neurodegeneration.
The article draws attention to the influence of non-coding RNAs, including lncRNAs, circRNAs, and enhancer RNAs, in modulating R-loop formation. These RNA species can either stabilize or destabilize R-loops, thus influencing chromatin structure and transcriptional dynamics. Additionally, the interplay between R-loops and RNA modifications like m6A and m5C further adds to the complexity of their biological impact, especially in DNA repair pathways.
The emerging connection between R-loops and immune responses are also explored, showing how they can activate pathways like cGAS-STING, linking genomic surveillance to inflammatory signaling. This cross-disciplinary significance makes R-loops a promising frontier for therapeutic intervention, especially in diseases driven by genome instability.
# # # # #
Genes & Diseases publishes rigorously peer-reviewed and high quality original articles and authoritative reviews that focus on the molecular bases of human diseases. Emphasis is placed on hypothesis-driven, mechanistic studies relevant to pathogenesis and/or experimental therapeutics of human diseases. The journal has worldwide authorship, and a broad scope in basic and translational biomedical research of molecular biology, molecular genetics, and cell biology, including but not limited to cell proliferation and apoptosis, signal transduction, stem cell biology, developmental biology, gene regulation and epigenetics, cancer biology, immunity and infection, neuroscience, disease-specific animal models, gene and cell-based therapies, and regenerative medicine.
Scopus CiteScore: 7.3
Impact Factor: 6.9
# # # # # #
More information: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/
Editorial Board: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/editorial-board/
All issues and articles in press are available online in ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/genes-and-diseases ).
Submissions to Genes & Disease may be made using Editorial Manager (https://www.editorialmanager.com/gendis/default.aspx ).
Print ISSN: 2352-4820
eISSN: 2352-3042
CN: 50-1221/R
Contact Us: editor@genesndiseases.com
X (formerly Twitter): @GenesNDiseases (https://x.com/GenesNDiseases )
# # # # # #
Reference
Min Zhu, Xinyu Wang, Hongchang Zhao, Zhenjie Wang, Update on R-loops in genomic integrity: Formation, functions, and implications for human diseases, Genes & Diseases, Volume 12, Issue 4, 2025, 101401, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101401
Funding Information:
National Natural Science Foundation of China 32201061
Natural Science Foundation of Shandong, China ZR2021QC083
Genes & Diseases Editorial Office
Genes & Diseases
+86 23 6571 4691
editor@genesndiseases.com
Distribution channels:
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.
Submit your press release